Scaling Bitcoin: Analyzing BTC-based Layer 2 Solutions and Their Impact on the Future of Cryptocurrency

Why Bitcoin needs to scale
It's been a long time since Bitcoin was a geek toy from the era of ThePirateBay, Apple of Steve Jobs' time, when you could spend a handful of BTC on your home PC on pizza, and when Green Day, Bring Me The Horizon, Ryanna, and Chester Bennigton we're blasting the hits from the speakers, and Chester Bennigton was charging the youth at the stadiums. And just outside the window the global financial crisis had just hit. And the more Bitcoin became widespread, the more urgent the issue of its scaling became. After all, the more users - the more on-chain activity. And the more users - the more expensive the scarce asset, which attracts even more users to digital gold.
The reason why the Bitcoin blockchain can only handle 7-10 transactions per second is that Bitcoin blocks are created on average every 10 minutes, and each block can contain a limited number of transactions.
The block time, a 10-minute interval between bitcoin blocks, was set when bitcoin was created and is not likely to change in the future. However, the limit on the size of each block has changed several times. In 2010, Satoshi Nakamoto set a rule that a block size could not exceed 1MB. In 2017, this limit was changed thanks to the SegWit update, which increased the limit to 4MB. However, most bitcoin blocks are still around 1.3MB in size.
These limits are set by the Bitcoin network to prevent the blockchain from growing in size too quickly, so they are not likely to change in the future. Thus, most efforts to increase the scale of the Bitcoin blockchain are aimed at reducing the amount of data required for Bitcoin transactions. For example, the Taproot update introduces more efficient transactions that take up less space on the Bitcoin blockchain. But these innovations came much later than Bitcoin itself, not even years later, but a decade later. Hasn't anyone thought about scaling and BTC L2s before the 2020s?
And how do you scale a system that can actually perform only the simplest of actions of transferring funds from one wallet to another? It turns out that the story of scaling around Bitcoin has a big and fascinating history. Let's dive into it!
Early realisations of Bitcoin scaling
iDaemon
Back in 2012, Craig Wright began a project to create what was originally called the ‘iDaemon’, or Intelligent Daemon System, which is an elaborate design and architectural blueprint for a complex software system intended to scale Bitcoin to over 1 million transactions per second. This project includes various subsystems that manage various aspects of transaction processing, accounting, banking, exchanges, messaging and contracts in the context of a blockchain network, specifically Bitcoin.
And when compared to current L2 solutions, this was a complex project with many components and dependencies:
Moreover, iDaemon was a harbinger of modular architecture in the web3 world back in 2012! The modular nature of the architecture was planned to allow it to be customisable and scalable to meet consumer requirements, ensuring that the system remained practical and relevant in the dynamic landscape of digital money.
Despite its ambitious goals, iDaemon required significant resources and time, with development costs reaching approximately $900 million, and the project did not gain widespread adoption. But on 12 February 2024, Craig Wraith published an addendum to his iDaemon vision in which he pointed out that looking back from 2024, the Intelligent Daemon System has evolved significantly since 2015. And he is currently working on a system that is in the process of launching and will first scale to 1.5 million transactions per second and then grow according to the needs of the hardware to whatever the limit is.
Transition to BTC L2s
The Bitcoin Tier 2 (BTC L2) network solution (BTC L2) was created to address the scalability of the bitcoin network and high transaction fees. Back in 2015, Joseph Poon and Thaddeus Dryea proposed the concept of the Lightning Network, which is the most famous project to date. Lightning Network, by creating payment channels, implements fast and low-cost Bitcoin transactions, greatly improving the scalability of the Bitcoin network. Currently, the number of nodes and application scenarios of Lightning Network are rapidly evolving.
The Lightning Network primarily addresses the problems of low BTC payment speed and high cost, but does not address the lack of native BTC applications. Thus, during the same period, the concept of bitcoin sidechains (Sidechain) was proposed. Blockstream first proposed and developed a sidechain called Liquid Network, which was launched in 2018. Another protocol launched around the same time was RSK (Rootstock), which is better known than Liquid.
Due to the sheer amount of work and high technical complexity of BTC-based L2 development, RSK and Stacks gradually became one of the few projects in BTC L2 that could allow applications to be built on the Bitcoin network.
Lightning Network
The Lightning Network was first proposed in 2015 and began to be fully realised in 2018. With smart contracts, more transactions are possible. Lightning Network uses revocable sequential maturity contracts (RSMCs) and hashed time-locked contracts (HTLCs) to solve the confirmation and payment channel problems of offchain transactions.
Lightning Network has attracted widespread attention and adoption, but Lightning Network is mainly focused on Bitcoin payment scenarios. On 23 July this year, Lightning Labs, the developer of Lightning Network, announced a major update to Taproot Assets in Lightning Network, allowing Lightning Network to support multi-asset transfers in addition to BTC. Lightning Labs believes this update is hugely important and could help move the trillion dollar stablecoin market to Bitcoin, making the US dollar and the world's financial assets Bitcoin-based.
Rootstock
Rootstock (RSK) was first proposed in 2015 and officially launched in 2018. In addition to Rootstock, the team has developed various products based on RSK, including DEX, wallets, domain name services, and other dApps. These dApps are built on universal protocols and cover payments, storage, computing, communications and gateways/bridges. The goal is to create a comprehensive RIF (RSK Infrastructure Framework) ecosystem and unify it under RIF OS technology.
The Rootstock team is closely following the progress in the bitcoin ecosystem, especially the BitVM technology that underpins their upcoming BitVMX initiative. In addition, the team will focus on developing an RBTC super app between 2024 and 2025, consolidating their recent progress on DeFi tools on the Rootstock network.
Stacks
Stacks (formerly Blockstack) was first proposed in 2013 and had an initial coin offering (ICO) in 2017. The Stacks network uses the Proof of Transfer (PoX) consensus mechanism, which is an adaptation of the Proof of Burn concept and involves bitcoin miners transferring bitcoin to secure the Stacks blockchain and receive rewards.
On 28 August, after months of delays, Stacks launched the long-awaited Nakamoto update. The update will increase the speed of block production on the Stacks network by 120 times, reducing Bitcoin confirmation time from an average of 10 minutes to a few seconds. The update also prepares Stacks for the launch of sBTC, a ‘programmable bitcoin asset’ that will allow users to connect their BTC to the Stacks network in a relatively decentralised way. sBTC is expected to be finalised in September 2024.
These innovations have had a good impact on on-chain metrics in Stacks:
Despite the fact that Stacks is not a new technology, it shows great user activity in 2024 precisely because of the launch of sBTC. This shows that new BTC L2s projects are not only competing with each other, but also with teams that have been moving in the same direction for essentially the second decade. That sounds pretty mesmerising!
RGB
RGB is an offchain smart contract protocol based on the Bitcoin Lightning Network that allows participants in transactions on the Lightning Network channel to develop contractual agreements with or without the issuance of tokens. It was first proposed in 2019.
RGB is not necessarily a tokenisation protocol, but supports the issuance of smart contract tokens. RGB is an enhancement to coloured coins, which is a smart contract protocol that operates outside the Bitcoin blockchain, allowing users to perform smart contract transactions with significantly higher speed and lower fees. It uses the Bitcoin blockchain as the state capture layer, Bitcoin cryptocurrency as the ownership control system and zero-knowledge proof to achieve transaction privacy.
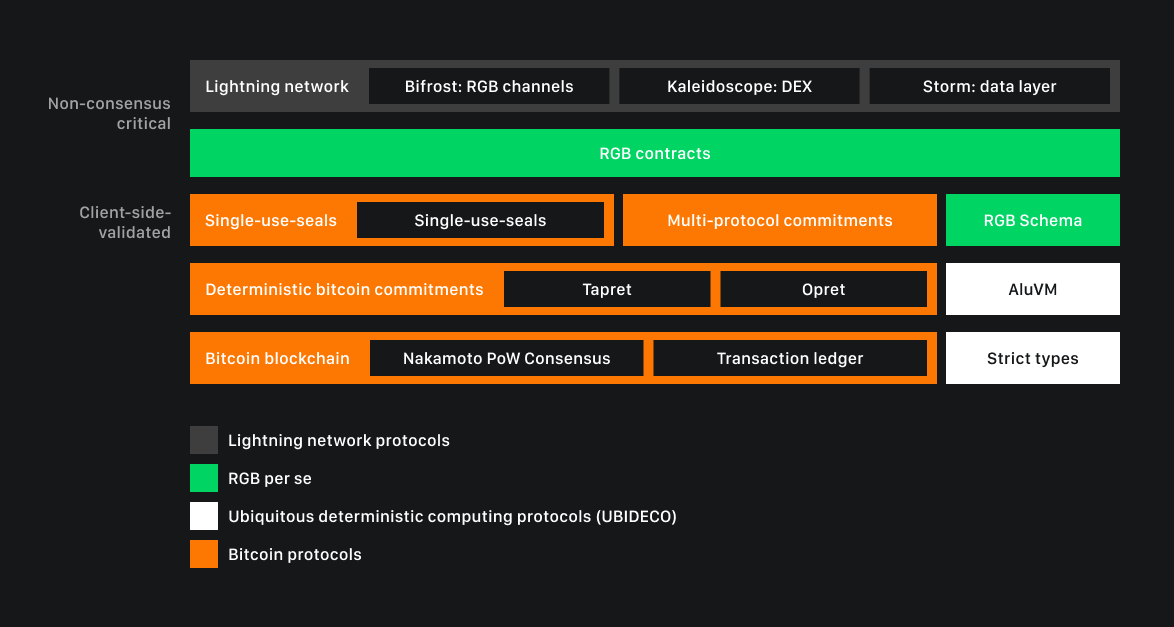
As an additional protocol capable of interoperating with Bitcoin and the Lightning Network, RGB represents an additional layer of programmability for the Bitcoin blockchain, allowing users to explore advanced blockchain-level automation while leveraging the Bitcoin architecture and paying even lower fees than other smart contract protocols such as ERC on Ethereum.
By taking advantage of the UTXO model, RGB++ Layer could create a new paradigm for asset issuance - allowing the same asset to be issued on multiple chains simultaneously, with different proportions issued on each chain. This would give asset issuers a high degree of flexibility. When a project team issues a token, they don't have to worry about losing users from one chain by issuing on another. Instead, they can issue a portion on BTC, a portion on BCH, and even a portion on the Dogecoin chain, extending their reach to communities across all UTXO chains.
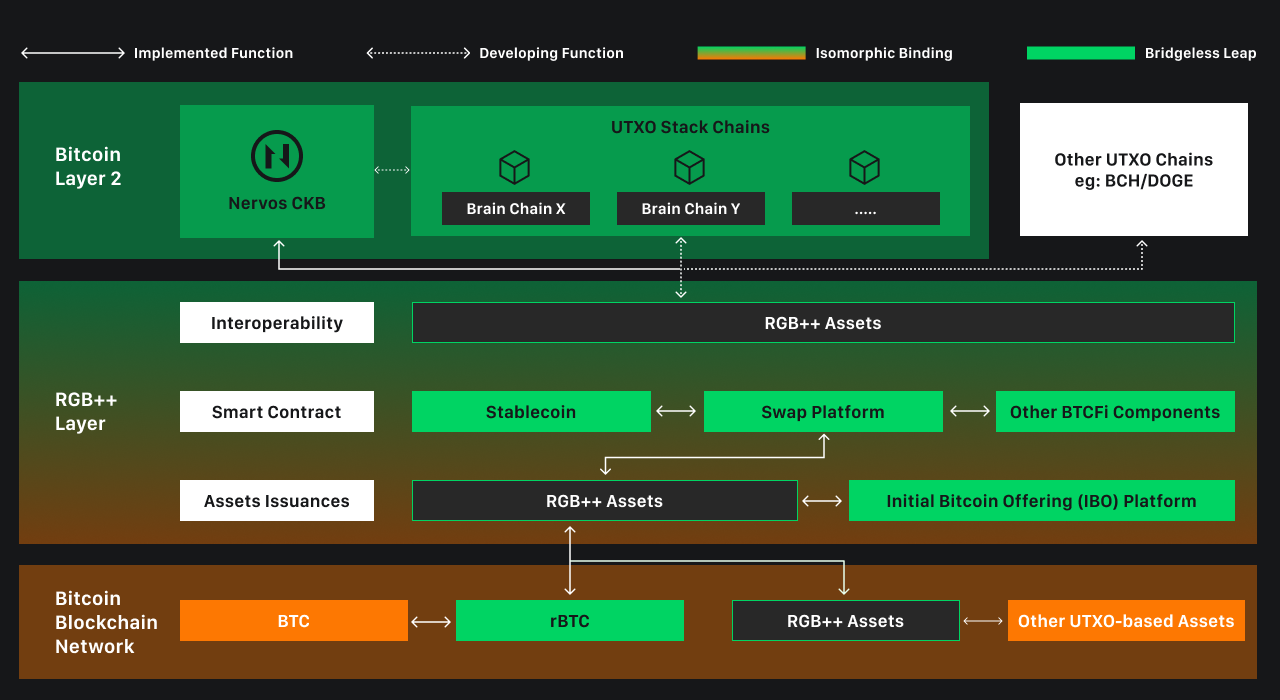
In addition, RGB++ Layer will introduce a brand new asset issuance model called Initial Bitcoin Offering (IBO). This can be seen as a launch pad for all RGB++ assets. The IBO platform supports direct pooling on UTXOSwap, a decentralised UTXO-based exchange that allows trading of newly released assets with high liquidity. The IBO issuance method strikes a balance between the VC model and the Fair Launch model, offering a more sustainable method. It avoids the problem of lack of community interest and also provides motivation for the project team.
Taproot
The Taproot update, activated in November 2021, was a key development for the Bitcoin ecosystem, opening up opportunities for sophisticated smart contracts, increased privacy and transaction efficiency. Building on the new Bitcoin Improvement Proposals (BIP), Taproot integrated Schnorr and Merkle Abstract Syntax Trees (MAST) technologies to enable the creation of more complex contracts and the hiding of transaction participants. This provided a significant increase in the programmability of the network and provided the basis for implementing operations such as staking, early contract termination and slashing mechanisms.
Key enhancements include BIP340 (multi-signature support), BIP341 (MAST implementation) and BIP342 (updated Tapscript programming language). These changes have simplified the creation of selective disclosure contracts, improved UTXO processing efficiency, and made the network more adaptive to future updates. As a result, protocols such as BTCFI have been empowered to interact with user assets in a scalable and efficient manner.
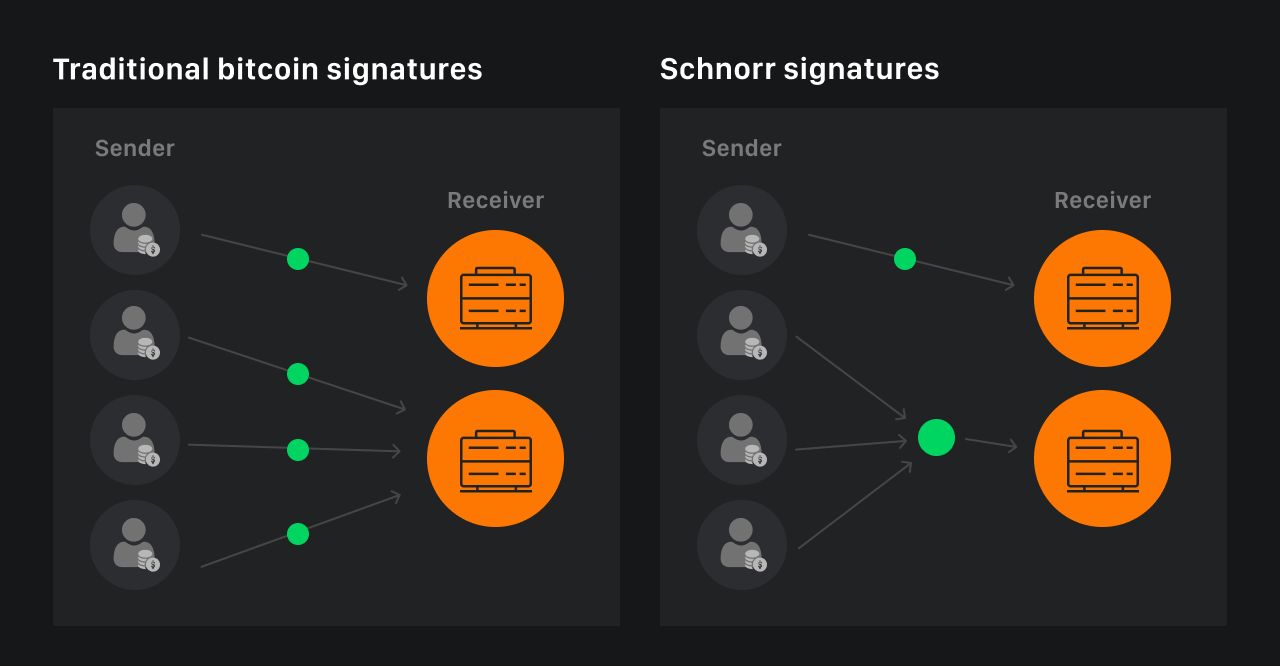
Taproot also laid the groundwork for ordinals, including the BRC-20 and ARC-20 token standards, using Taproot addresses (P2TR). This allowed metadata to be recorded on the blockchain more efficiently and economically, leading to increased use of the network for storing media files and other data. Taproot's adoption rate remains high (around 70%), emphasising its importance in the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem and its transition to new levels of functionality and scalability.
This has paved the way for new horizons and the development of a new generation of BTC L2s.
Fractal Bitcoin
Fractal Bitcoin enhances transaction processing capabilities and speed by recursively creating an infinite extension layer of the BTC main chain using BTC core code, while maintaining full compatibility with the existing Bitcoin ecosystem. According to the data, block confirmation time on the Fractal network is around 30 seconds and transaction processing performance is claimed to be 20 times faster than the BTC core chain.
The development team behind it, Unisat, is attracting the attention of the market. The entire team consists of developers who are well-versed in Bitcoin technologies such as SegWit, Lightning Network and TapRoot. The team's previous projects have also achieved good results on the BRC 20 trading market, and the $PIZZA token released by the team has also performed well in the market. Investors include Binance and OKX.
On 9 September, the Fractal Bitcoin mainnet was officially launched, bringing renewed excitement to the bitcoin ecosystem. As of 17:00 on 12 September, the number of FB addresses across the entire network reached 200,165, up 79,484 in the last 24 hours, and the number of active addresses reached 118,454.
BitVM
BitVM was introduced on 9 October 2023 in a white paper titled ‘BitVM: Compute Anything on Bitcoin’ authored by Robin Linus.
This concept offers a way to perform complex computations and smart contracts on the Bitcoin network without changing its consensus rules, extending the functionality of the blockchain. In August 2024, a second version, BitVM2, was introduced with an improved architecture and the ability to publicly verify transactions.
bitVM opens up new opportunities for decentralised finance (DeFi), smart contracts and other consumer applications, all based on the Bitcoin network. However, it also introduces a variety of new challenges for security and programmability, especially when translating these complex tasks into the restricted Bitcoin environment. Our research focuses on making bitVM production-ready , which includes ensuring security, optimising compilers, and building robust tools that will ensure that the entire bitVM ecosystem thrives, hopefully leading to mass adoption in the foreseeable future.
2024 - the boom of BTC L2s
Botanix
Launched by Botanix Labs in 2023, Botanix is a pioneering Bitcoin Layer 2 solution that integrates an Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)-equivalent layer atop the Bitcoin network. This innovative approach combines Bitcoin's robust security and decentralization with Ethereum's flexibility and programmability, enabling developers to seamlessly deploy decentralized applications (dApps) within the Bitcoin ecosystem.
At the core of Botanix is the Spiderchain, a decentralized network of multi-signature (multisig) wallets safeguarded by a randomized subset of participants known as Orchestrator nodes. This architecture ensures that Bitcoin bridged to the Botanix EVM is securely stored, allowing users to engage with dApps on the Botanix EVM while their assets remain protected.
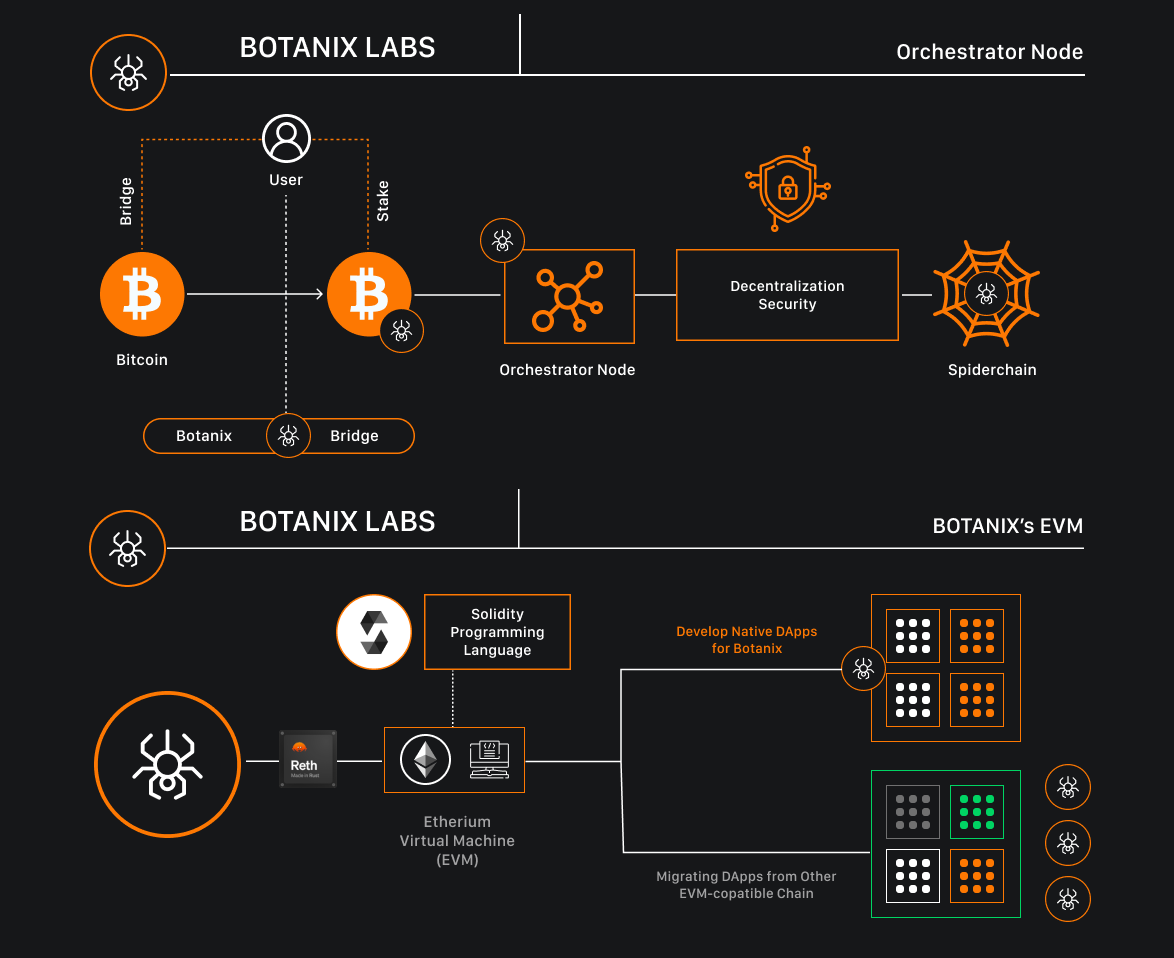
The Botanix EVM operates as a second-layer protocol on Bitcoin, facilitating activities such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs), lending, borrowing, and trading of non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Users can bridge their Bitcoin from the main Bitcoin network to the Botanix EVM, utilize it within various applications, and withdraw it back to the main layer as desired.
A significant milestone for Botanix Labs was the launch of the Aragog testnet in November 2023, marking the debut of the first fully decentralized EVM-equivalent Layer 2 on Bitcoin. This testnet provides developers with a platform to experiment and build applications, fostering the growth of a Bitcoin-native DeFi and NFT ecosystem.
Looking ahead, Botanix Labs has outlined a comprehensive roadmap that includes the implementation of permissionless staking and further decentralization of the Spiderchain network. These developments aim to enhance the scalability, security, and composability of the Bitcoin network, positioning Botanix as a catalyst for the evolution of programmable finance on Bitcoin.
In summary, Botanix represents a groundbreaking advancement in the Bitcoin ecosystem, merging the security and decentralization of Bitcoin with the programmability of Ethereum. By enabling the deployment of EVM-compatible dApps on Bitcoin, Botanix is set to unlock new possibilities for decentralized finance and beyond.
Merlin Chain
Launched by Bitmap Tech in February 2024, it is a Bitcoin Layer 2 solution combining a ZK-Rollup network, a decentralised oracle and a BTC fraud prevention module on the chain. Bitmap Tech's metaversion platform, Bitmap.Game, and the BRC-420 asset protocol have received very good feedback in the market this year.
At the end of August, interoperability infrastructure ZK Polyhedra Network announced the integration of its decentralised verification network (DVN) with Merlin Chain via LayerZero. Once the integration is complete, more than 100 Merlin application ecosystems will benefit from ZK's secure interoperability.
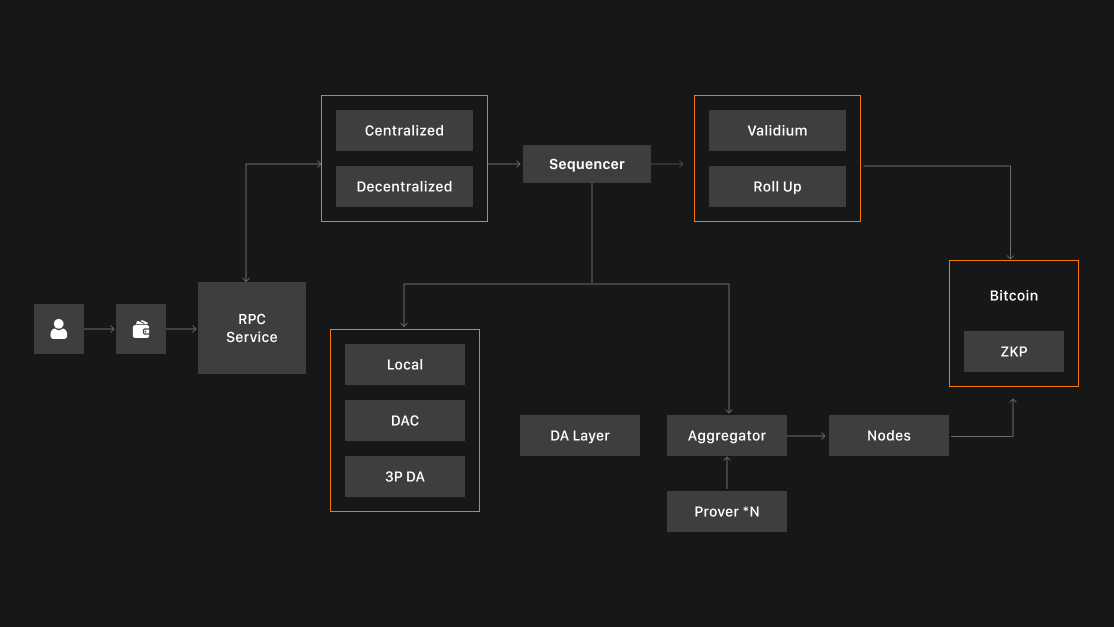
On 9 September, Merlin Chain published its semi-annual report, which looks at its growth trajectory in the first half of 2024, including: $1.2b TVL, $16b bridge volume, 1.9m addresses on the chain, 12.7m transactions; 50 days after mainnet launch, TVL exceeded $3.9b (88% of which was proprietary assets such as BTC and warrants) and M-BTC market value reached $1.2b in H1; asset trading volume exceeded $3b and DEX liquidity exceeded $78m. It is reported that in the second half of the year, Merlin Chain plans to continue to work hard in the three aspects of technology, ecology and community to promote the sustainable development of the bitcoin ecosystem.
Also, Merlin Chain's proposed decentralised oracle network uses a distributed system in which sequencer nodes collect and compress transaction data, ZK state roots and proofs, which are then compiled by the oracle network and uploaded to Bitcoin. This ensures that the data is publicly available, and fraud protection mechanisms provide final validation in Bitcoin. While the original data is stored off-chain, the state roots are tied to Bitcoin, allowing users to receive and verify transactions through ZKP. The network supports $BTC, $MERL and BRC-20 asset staking, while smart contracts automate staking and rewards, providing real-time monitoring and flexible withdrawal options.
BitLayer
Bitlayer has become a dominant force in the Bitcoin Layer 2 market. It currently ranks second among bitcoin sidechains with a TVL of over $500 million and a market share of 21.78%. The platform's impressive growth is evidenced by a 71.64% increase in TVL over the last week and an 88.67% increase over the last month. This rapid growth outpaces most competitors in the bitcoin sidechain ecosystem and demonstrates the market's high confidence in Bitlayer's approach.
Bitlayer's solution synthesises the technical characteristics of BitVM, DLC and various XVMs (such as EVM, CairoVM, SolVM, MoveVM), addressing three main challenges: First-level verification, asset pairing, and enrichment of state transition expressions.
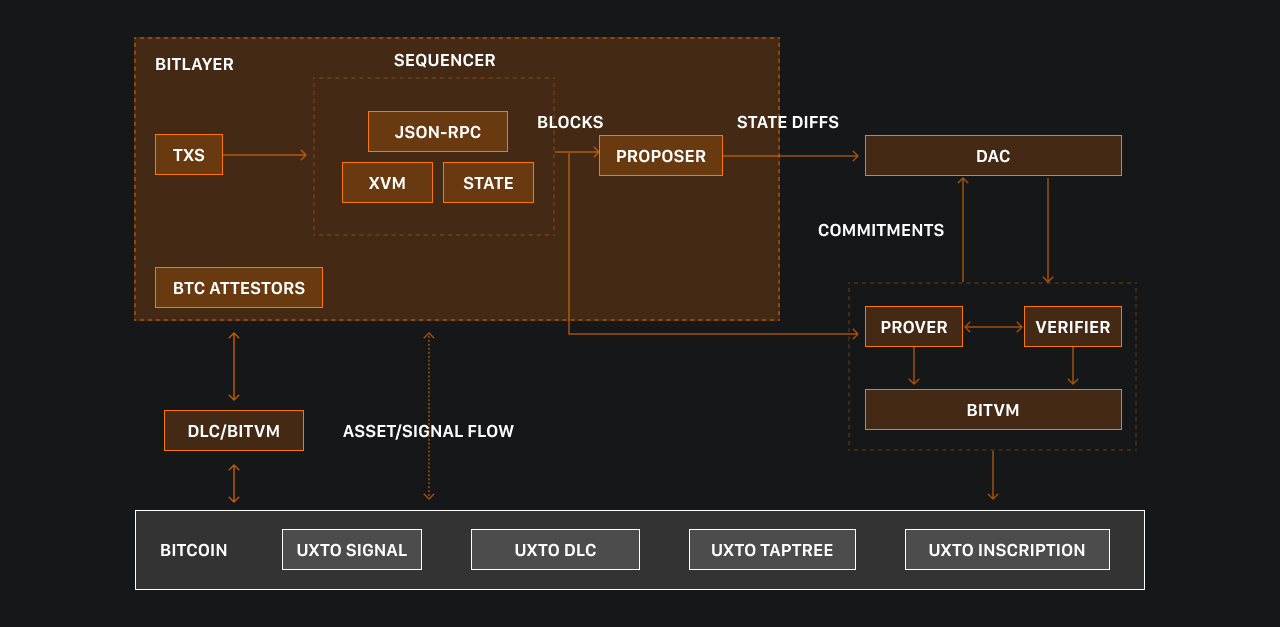
Architecturally, Bitlayer is a fairly typical example of the Rollup-equivalent model. In order to adapt to Bitcoin's unique programming model, BitVM was introduced as a component to solve state-related problems. In addition, DLC|BitVM was included as a cross-chain component for messaging/asset exchange, and the XVM component of the sequencer can, in theory, support any Turing-complete programming language.
exSat
Launched by the exSat Network in April 2024, exSat is a pioneering Docking Layer designed to enhance Bitcoin's scalability and interoperability by bridging the Bitcoin mainnet with various Layer 2 (L2) scaling solutions.
Unlike traditional L2 solutions that primarily focus on speed and cost reduction, exSat introduces a unique architecture that maintains Bitcoin's robust security while enabling seamless interaction with decentralized applications (DApps), smart contracts, and cross-chain solutions. At the core of exSat's innovation is its hybrid consensus mechanism, which combines Bitcoin's Proof of Work (PoW) with a staking-based Proof of Stake (PoS) system. This integration extends Bitcoin's data consensus, enhancing trust and security across the ecosystem.
A key component of exSat's infrastructure is the Decentralized State Data Indexing, which leverages EOS RAM for efficient on-chain storage and processing of Bitcoin's Unspent Transaction Outputs (UTXOs). This setup ensures that smart contracts can operate seamlessly, supporting diverse assets such as BTC, Ordinals, and Runes.
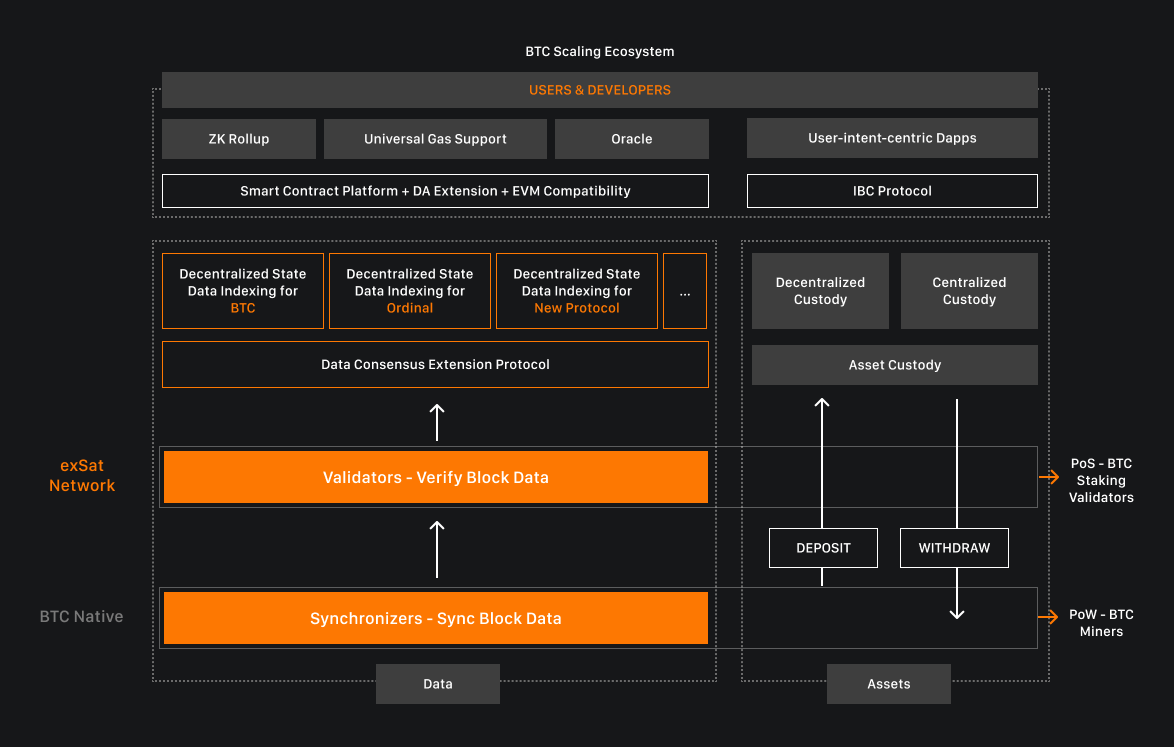
Developers benefit from exSat's full support for Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)-based application development, enabling the creation of a wide range of DApps within the Bitcoin ecosystem. This compatibility facilitates the deployment of decentralized exchanges (DEXs), lending platforms, and NFT marketplaces, all while utilizing Bitcoin's security framework.
To ensure network security and integrity, exSat employs Synchronizers and Validators. Synchronizers, typically BTC mining pools, upload the latest Bitcoin blocks to the exSat network, while Validators—users staking a minimum of 100 BTC—verify the validity of the uploaded data. This collaborative approach maintains a decentralized and trustworthy environment for data consensus.
SatoshiVM
SatoshiVM is a Bitcoin L2 rollup with ZKP that is compatible with the EVM ecosystem. According to the project (at the time of writing) over 4,500 bitcoins have been connected to the network and around 480,000 unique wallets have interacted with the network.
SatoshiVM runs an execution layer that uses rollups to batch process transactions and send them to the Bitcoin network for final settlement. This allows SatoshiVM to achieve much faster transaction speeds, while saving users money and maintaining sufficient decentralisation and good security. The network's native token is bitcoin, and gas fees on SatoshiVM are also paid in bitcoin.
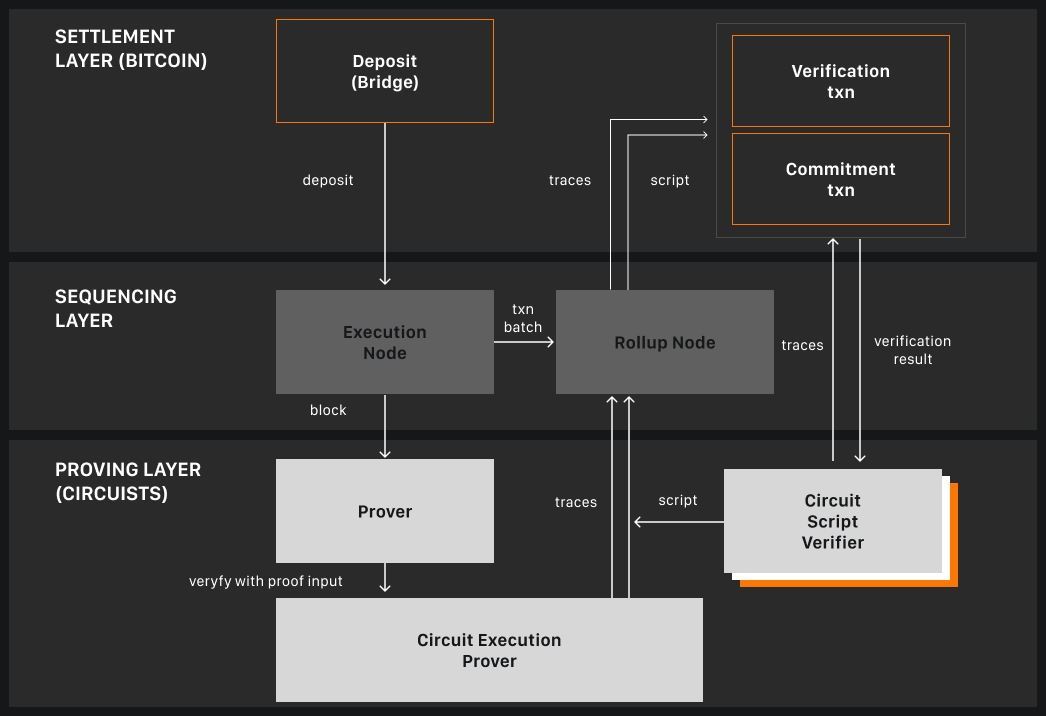
Using this approach, SatoshiVM expands the use of Bitcoin and the application of the Bitcoin network. Bitcoin connected to the network can be used in DeFi applications on the network. It is also capable of performing other complex operations such as inscriptions (SARC20). As of now, SatoshiVM is still in the testing phase.
BOB Hybrid Layer 2 Solution
BOB, a hybrid Layer 2 solution for Bitcoin, enhances scalability and functionality by integrating Bitcoin's security with Ethereum's programmability. Launched on May 1, 2024, BOB enables the creation of decentralized applications (dApps) that leverage both blockchain technologies.
The BOB hybrid layer 2 solution is designed to leverage the robust security of Bitcoin while integrating the flexible functionalities typically associated with Ethereum’s ecosystem. According to the Hybrid L2 Vision Paper, BOB aims to tackle the scalability challenges of DeFi applications on Bitcoin, fostering a more efficient environment for developers and users alike. This architecture allows for the seamless creation of decentralized applications (dApps) that can benefit from the strengths of both blockchain technologies.
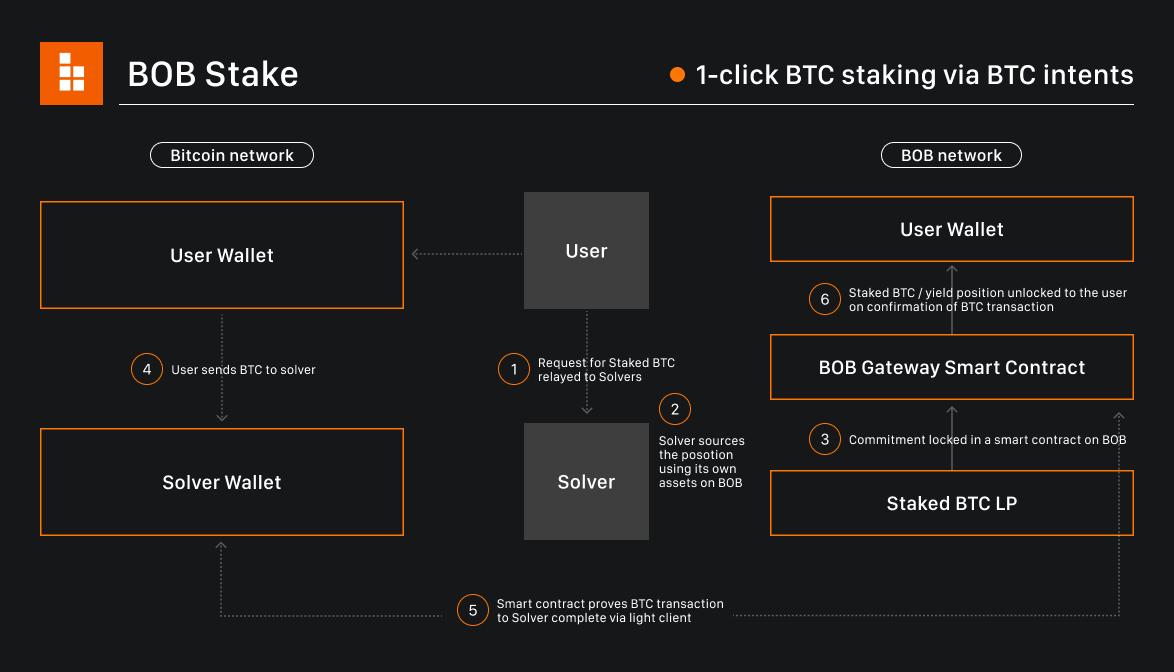
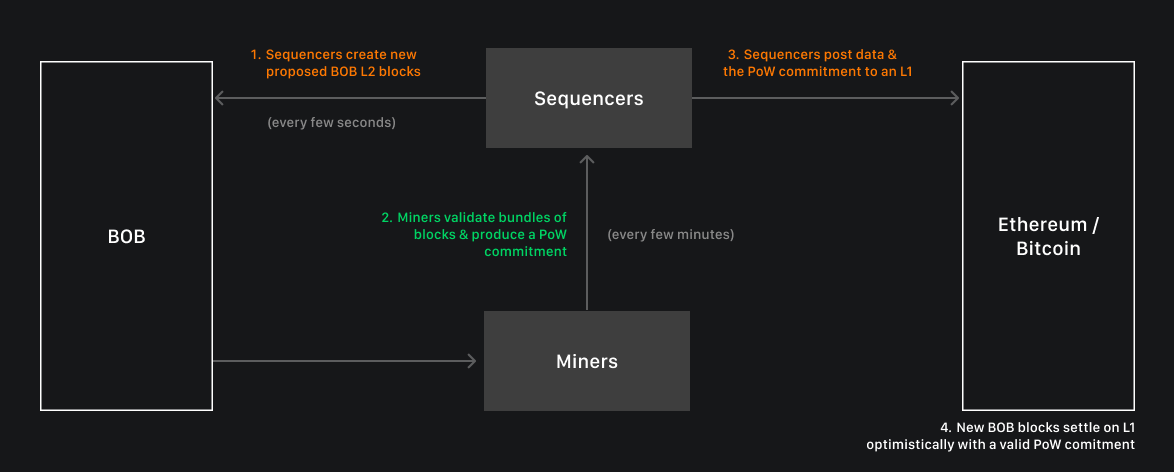
As described in the Trust Machines blog, BOB launched on May 1 and represents a significant shift in how Bitcoin can be utilized, effectively bridging the gap between two powerful blockchain networks. This initiative not only enhances Bitcoin's functionality but also aims to attract a wider user base by enabling features typically reserved for platforms like Ethereum, thus aiming to onboard the next billion users to Bitcoin.
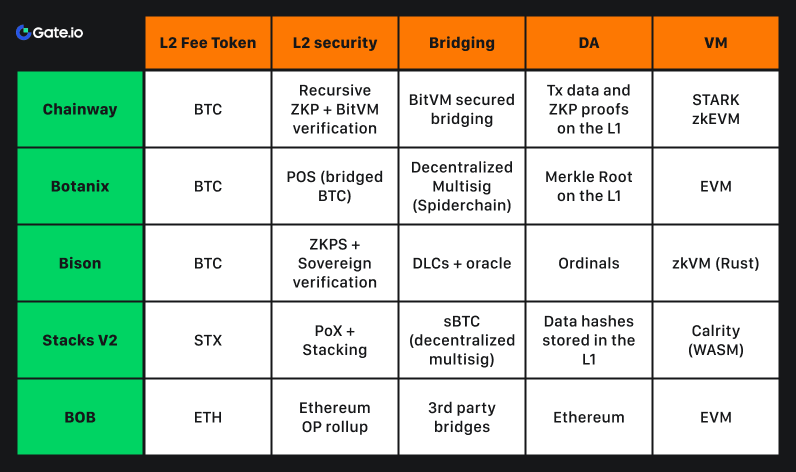
High-level comparison of some BTC L2s:
Conclusion: The Importance of Scaling Bitcoin
Bitcoin's current scalability challenges primarily arise from its limited transaction processing capabilities, leading to congestion, higher fees, and slower confirmation times, particularly during periods of peak network activity. As the cryptocurrency market continues to mature, with forecasts indicating that the total market value could exceed $8 trillion by 2025, scaling becomes vital for mainstream adoption.
Layer 2 solutions like BOB and Stacks are leading the charge in addressing these concerns. BOB, which integrates the Babylon protocol, not only aims to enhance transaction efficiency but also supports a massive BTC staking initiative, pushing DeFi adoption on Bitcoin further. Meanwhile, Stacks continues to innovate by enabling smart contracts on Bitcoin, thus expanding its functionality and appealing to a wider investment base.
Moreover, other emerging projects in 2024 are focusing on unique features that promote user experience and optimize transaction processes, further diversifying the Layer 2 landscape on Bitcoin. According to predictions from multiple analysts, such as those reported in Forbes, the increasing adoption of innovative L2 solutions will play a crucial role in attracting institutional involvement and legitimizing Bitcoin as a financial asset.
Without significant advancements through these Layer 2 technologies, Bitcoin risks losing competitive ground against other cryptocurrencies that boast better scalability solutions. The urgency for robust infrastructure to handle an increasing transaction volume while keeping security at its core remains a top priority to ensure Bitcoin's continued relevance and growth in an evolving digital currency landscape.
About Yona Network
Yona is a real-time latency Bitcoin L2 blockchain enabling Web2 experience for dApps. We use custom hyper-optimized modularized SVM to achieve superior performance with less than 10ms latency and block time. Yona enables lightning-fast transactions and offers limitless scalability, paving the way for next-generation protocols tailored to enhance the user experience within the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Yona Network links:
Website | Documentation | Twitter | Discord | Blog

