Yona Network integrates with BTC restaking protocol Babylon Chain
Yona Network are pleased to announce an integration with Babylon Chain to bridge the worlds of BTC and Solana.
Yona and Babylon integration explained
Yona Network and Babylon Chain are integrating to bridge the worlds of Bitcoin and Solana VM. Yona Network is the fastest Bitcoin L2 powered by Solana Virtual Machine (SVM). SVM offers superior performance (over 10,000 transactions per second) compared to EVM, making it an ideal foundation for building DeFi infrastructure for Bitcoin assets with money markets, fastest on-chain order books and oracles. Yona Network brings the fastest execution layer to Bitcoin – the blockchain that holds over $1 trillion in assets.
From Yona’s side, this integration brings the security, speed, scalability, and user experience of Solana into the BTC ecosystem. On Babylon’s side, this allows the integration of BTC crypto-economic security delegation into Yona Network through Babylon Chain’s restaking technology. Combining the economic and decentralized power of Bitcoin with the technological innovations of Yona and Babylon elevates the advancement of Bitcoin L2’s to a new level! As integration deepens, we expect a new wave of primitives and innovations at the intersection of Bitcoin and Yona Network’s SVM.
One of the pain points for Bitcoin L2 is the need for crypto-economic security to launch the chain, which Babylon’s technology addresses. Validators can lock BTC stakes directly for restaking in Babylon, which can be slashed in case of attack attempts using forks or malicious behavior. With Bitcoin’s unmatched reliability and value, along with Babylon’s technology, Yona validators can quickly unbound in a few hours instead of days and weeks. This all comes together to create a complementary synergy.
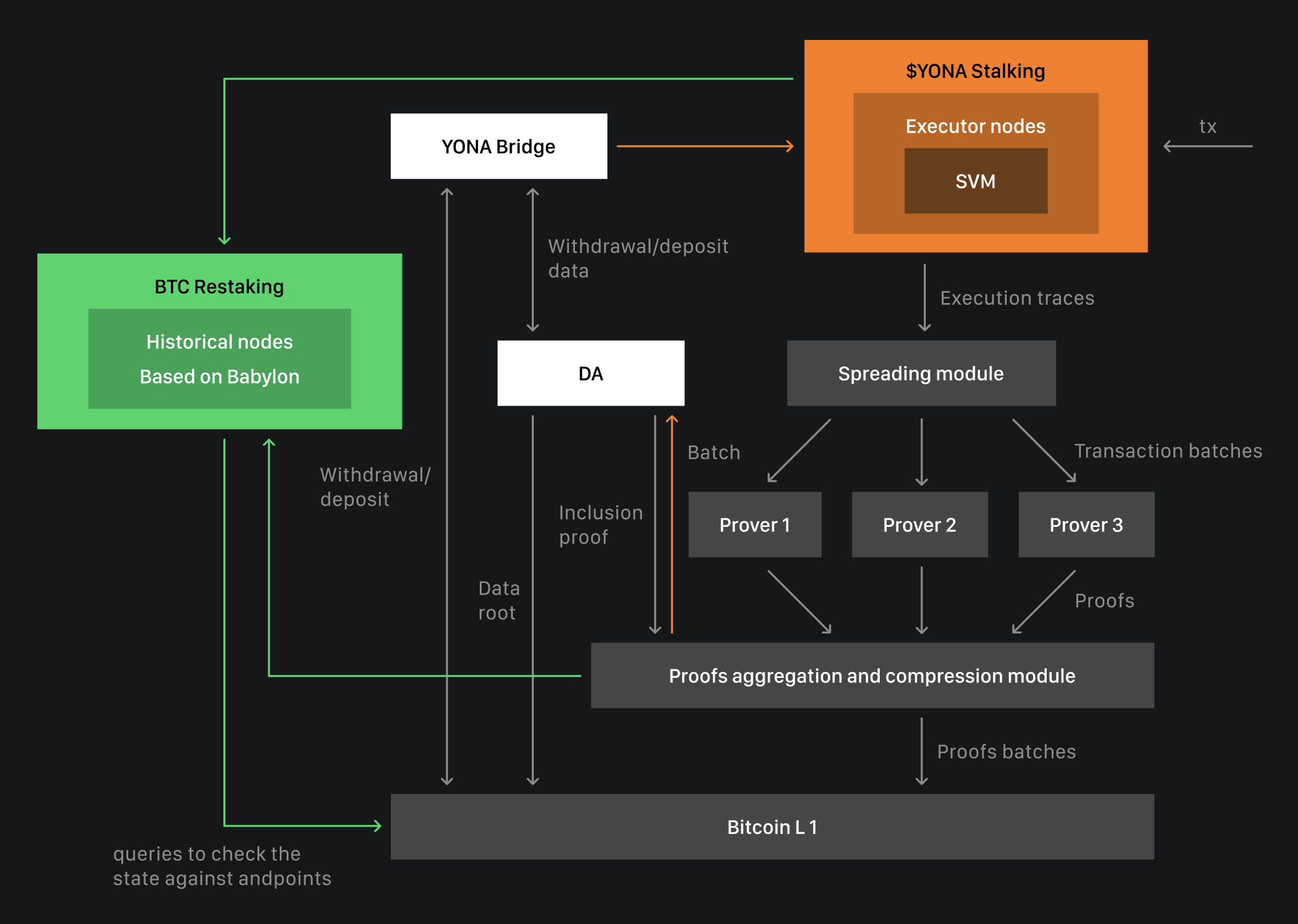
Additionally, users of the Yona ecosystem will be able to stake BTC through Babylon to secure Yona Network and other networks, including those in the Bitcoin ecosystem. This approach enhances BTC utilization, benefiting the entire Bitcoin ecosystem by driving the adoption of new technologies and primitives. Since Babylon is a Cosmos-based chain, Yona Network may also gain access to the Cosmos network and IBC technology through Babylon’s cross-chain integrations. As the Yona ecosystem develops, it will provide the infrastructure for creating and utilizing Babylon-based LRTs.
What is Babylon Chain and why it's of strategic importance to the Yona Network.
Babylon Chain holds strategic significance for Yona Network due to its role in the Bitcoin ecosystem. The Babylon team faced a unique challenge: enabling BTC restaking in a Bitcoin PoW network to create a primitive for delegating crypto-economic security.
Babylon originated from research on Bitcoin's security, specifically a seminal paper co-authored by Babylon co-founders David Tse and Fisher Yu, EigenLayer founder Sriram Kannan, and other collaborators. The core idea of Babylon is to scale the security of the BTC network, which operates as a PoW network unlike PoS networks like Solana and Ethereum. As of July 2024, Bitcoin has $1.15 trillion in locked value, making it the largest economic network. Some researchers believe PoW is more resilient to forks than PoS.
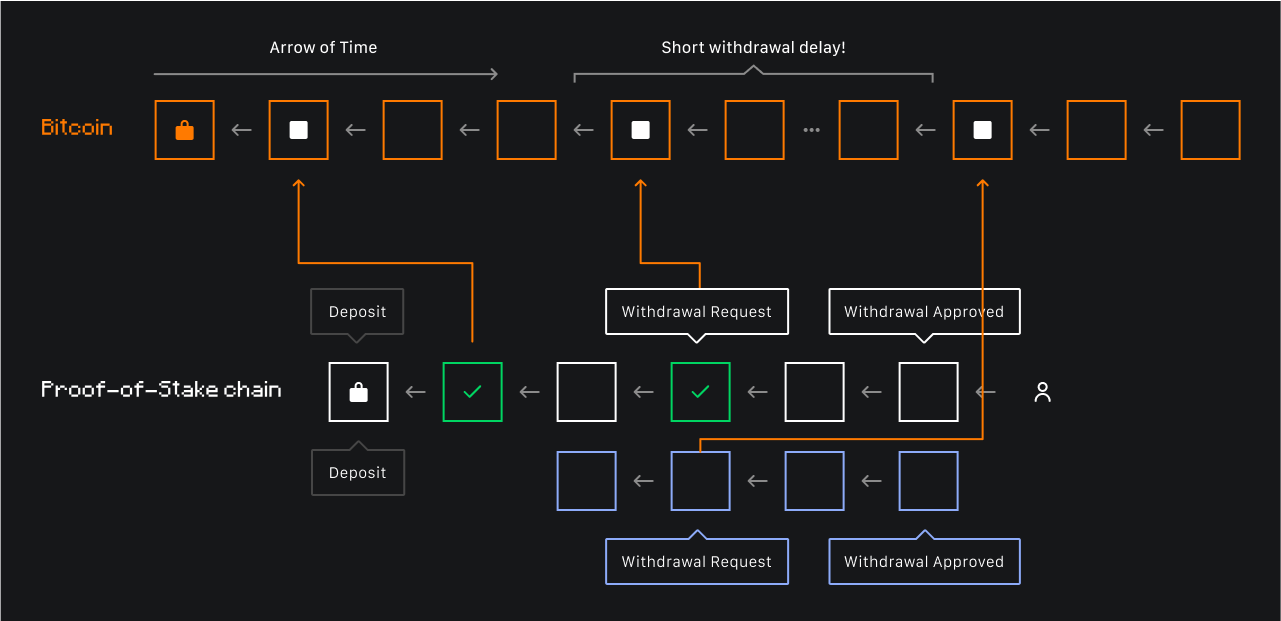
In particular, the combination of PoW and Bitcoin’s market capitalization makes it well-suited for delegating crypto economic security and ensuring the correctness of timestamps to counter forks. In a PoW network, creating a longer chain than the canonical one is impossible without controlling more than 51% of the total hash rate. Consequently, Bitcoin's network, being the most reliable and secure, can forgo certain PoS network primitives, such as long unbounding periods for stakes, which in PoS networks can sometimes take several days.
But if user directly connect Cosmos and BTC by timestamps, two problems arise:
- The BTC block time is about 10 minutes, while the Cosmos network creates approximately 60 blocks in that time.
- Each of these 60 blocks requires a separate timestamp, resulting in (32+32)*60=3840 bytes of space, which requires at least 48 OP_RETURN transactions. The complexity increases if multiple blockchains are recording checkpoints.
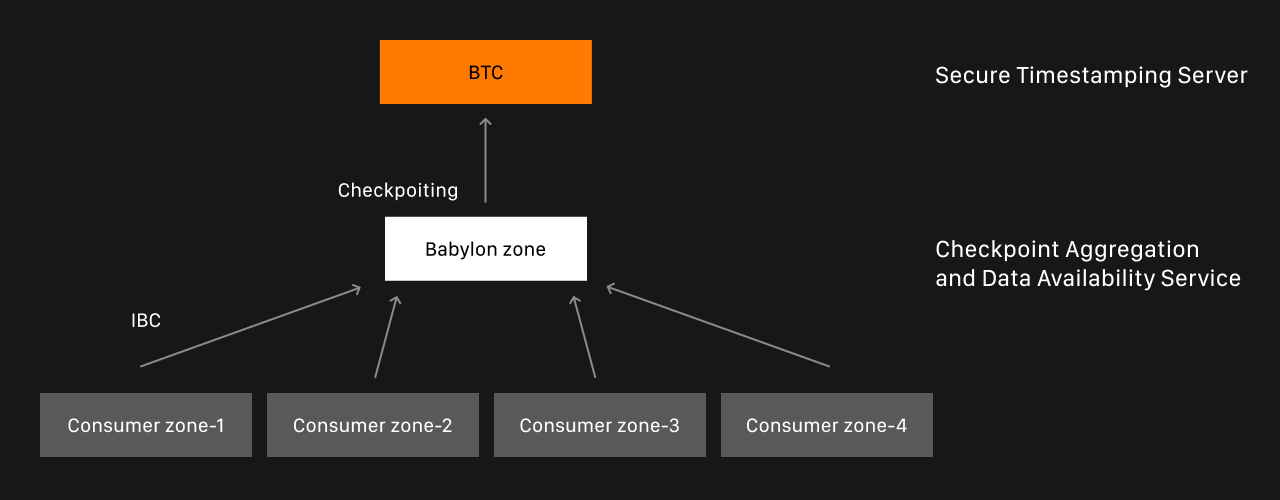
This is where Babylon Chain comes into play. Babylon, built with the Cosmos SDK, collects and aggregates checkpoints from PoS networks that want to record checkpoints in the Bitcoin network and writes them into the BTC network. Babylon Chain acts as an intermediary across multiple networks, enabling them to leverage Bitcoin’s robust security using timestamps. Additionally, Babylon allows Cosmos to reach a resilience threshold of up to 51% versus the standard 1/3 validators, which can be sufficient for partial interference in block finalization. This is achieved by modifications in the Cosmos-based Babylon chain, which receives checkpoint streams from multiple PoS chains as transaction data and sends a unified checkpoint stream to Bitcoin on their behalf.
Another part of Babylon is the protocol for Bitcoin staking. This protocol allows Bitcoin, the asset, to provide economic security to any decentralized systems through trustless (and self-custodian) staking. The Babylon Bitcoin staking protocol allows Bitcoin holders to stake their bitcoins for PoS blockchains without requiring any third-party custody/bridge/wrap.
Thus, the full architecture of Babylon consists of three blockchains:
- PoS client chains (e.g., Cosmos consumer zones)
- Babylon
- Bitcoin
Thus, the Yona Network and Babylon teams are exploring integration opportunities, particularly because Babylon reduces the unbonding period for PoS chains from weeks to a few hours, allowing these chains to use Bitcoin as a timestamping service, similar to the role of social consensus. Bitcoin staking also adds a huge source of economic security and potential users as well as potential liquidity via liquid staking tokens. This creates attractive participation conditions for operators and delegators. Additionally, Babylon's architecture prevents long-range attacks using the k-deep slashing rule for unbonding validators and ensures the reduction of an adversary's stake in the event of short-range security attacks.
Babylon chain links:
Website | Documentation | Twitter | Discord | Blog
What is Yona?
Yona is the fastest modular Bitcoin L2 based on SVM with a blockchain holding assets worth over $1T. Yona enables lightning-fast transactions and offers limitless scalability, paving the way for next-generation protocols tailored to enhance the user experience within the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Yona Network links:
Website | Documentation | Twitter | Discord | Blog

